NASA MESSENGER Image of Mercury: Hovnatanian Crater
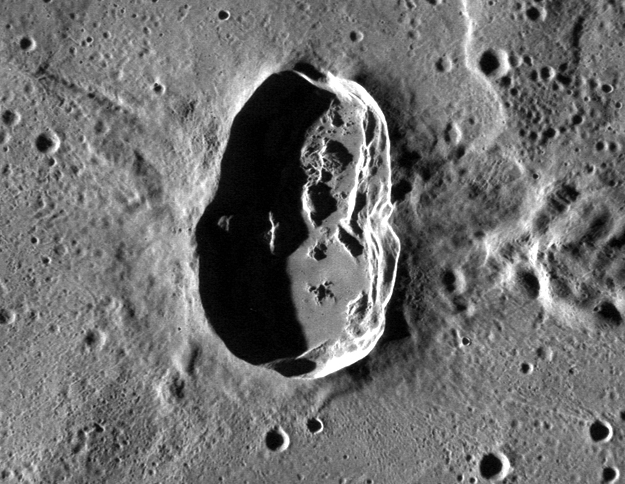
Of Interest: Hovnatanian crater was formed by an object that impacted at a very oblique angle, causing the crater to appear elliptical. Although impacts at most angles produce circular craters, impacts with incidence angles <15o (from the horizontal) will create elliptical craters. The rays of Hovnatanian form a "butterfly" pattern, which also indicates an oblique impact.
This image was acquired as a high-resolution targeted observation. Targeted observations are images of a small area on Mercury’s surface at resolutions much higher than the 250-meter/pixel (820 feet/pixel) morphology base map or the 1-kilometer/pixel (0.6 miles/pixel) color base map. It is not possible to cover all of Mercury’s surface at this high resolution during MESSENGER’s one-year mission, but several areas of high scientific interest are generally imaged in this mode each week.
The MESSENGER spacecraft is the first ever to orbit the planet Mercury, and the spacecraft’s seven scientific instruments and radio science investigation are unraveling the history and evolution of the Solar System’s innermost planet. Visit the Why Mercury? section of this website to learn more about the key science questions that the MESSENGER mission is addressing. During the one-year primary mission, MDIS is scheduled to acquire more than 75,000 images in support of MESSENGER’s science goals.
Credit: NASA/Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory/Carnegie Institution of Washington. Larger image
Date acquired: January 16, 2012
Image Mission Elapsed Time (MET): 235218286
Image ID: 1273501
Instrument: Narrow Angle Camera (NAC) of the Mercury Dual Imaging System (MDIS)
Center Latitude: -7.7°
Center Longitude: 172.6° E
Resolution: 58 meters/pixel
Scale: Hovnatanian crater is approximately 33 km (21 mi.) long.
Incidence Angle: 77.3°
Emission Angle: 55.6°
Phase Angle: 132.9°








