NASA Space Station On-Orbit Status 22 September, 2021 – New European Robotic Arm Outfitted
Russia’s Nauka multipurpose laboratory module continues being outfitted today before operations begin with Europe’s new robotic arm.
In the meantime, three Expedition 65 crewmates are preparing to move their Soyuz crew ship to a new port on the International Space Station next week.
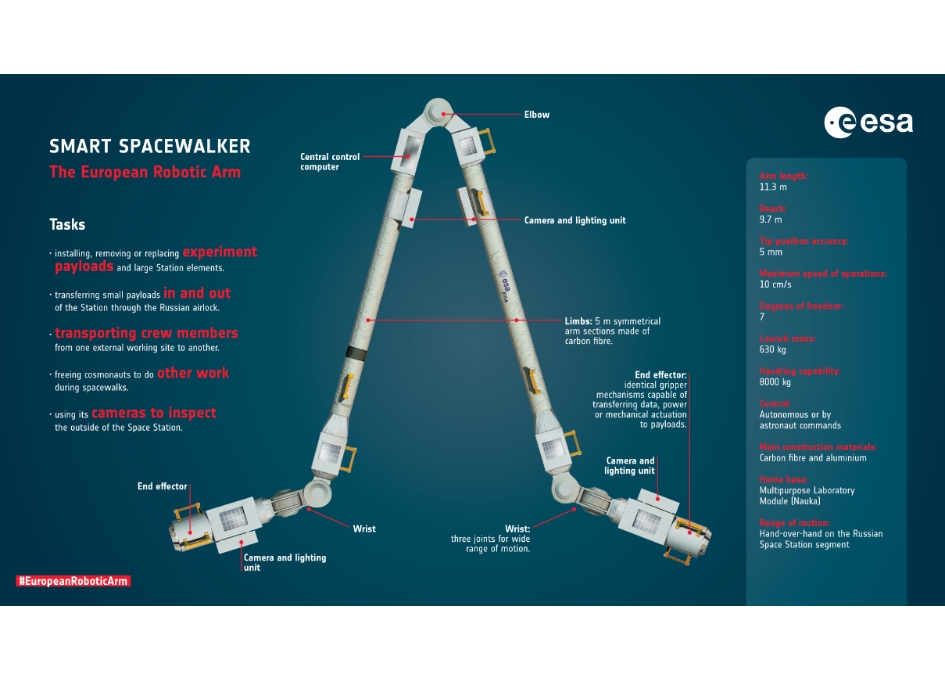
Soon, there will be three robotic arms from three different countries operating on the orbiting lab. The newest arm, the European robotic arm (ERA), was delivered in July attached to Nauka. ESA (European Space Agency) Flight Engineer Thomas Pesquet joined Roscosmos Flight Engineer Pyotr Dubrov inside Nauka today and configured ERA controller hardware and software. The other two robotic manipulators are Japan’s robotic arm which services the Kibo laboratory module, and the Canadarm2 robotic arm which captures and installs spaceships, maneuvers spacewalkers, and performs other fine-controlled tasks on the station.
The three NASA Flight Engineers, Megan McArthur, Shane Kimbrough, and Mark Vande Hei, worked in the station’s U.S. segment on science and maintenance activities throughout Wednesday. Commander Akihiko Hoshide of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) worked primarily in the Kibo laboratory module on space biology activities.
McArthur started her day replacing fuel bottles inside the Combustion Integrated Rack before swabbing microbe samples from station surfaces for later analysis. Kimbrough disassembled an old device that measured electrical charges building up around the station’s main solar arrays. Finally, Vande Hei serviced communications hardware inside Kibo then moved on and switched samples inside the Materials Science Laboratory.
Three-time Roscosmos Flight Engineer Oleg Novitskiy checked components inside the Soyuz MS-18 crew ship today before it moves to a new port next week. He will be flanked by Vande Hei and Dubrov inside the Soyuz when it undocks from the Rassvet module on Thursday, Sept. 30, at 8:21 a.m. EDT. They will dock less than 45 minutes later to Nauka for the first time.
On-Orbit Status Report
Payloads:
Cool Flames Investigation with Gases: A crewmember replaced the Manifold #4 fuel bottle with a new bottle containing 100% Butane. Cool diffusion flames were discovered during droplet combustion experiments aboard the ISS in 2012, and this initiated a rapidly growing field of combustion research. A cool flame is one that burns at about 600 degrees Celsius. A typical candle is about two times hotter, burning at around 1,400 degrees Celsius. Most internal combustion engines are designed using computer models that neglect cool flame chemistry, but ignition and flame propagation in engines depend on cool flame chemistry. Cool flame chemistry also has a significant impact on fuel octane and cetane numbers, whose understanding has large economic consequences.
Dreams: A crewmember doffed the DREAMS headband and configured it for data downlink to the ground. The hardware was then stowed. Sleep plays a major role in human health and well-being. Insufficient sleep, or sleep disorders can increase the risk of developing medical conditions, such as cardiovascular diseases, and can impair task performance. The Sleep Monitoring in Space with Dry-EEG Headband (Dreams) is a technology demonstration investigation that utilizes the Dry-EEG Headband: an effective, affordable, and comfortable solution to monitor astronaut sleep quality during long-duration spaceflight aboard the International Space Station (ISS).
Human Research Facility-2 (HRF-2): A crewmember removed old HRF Rack drawer handles from an HRF Rack 2 drawer location and replaced them with new handles. HRF-2 provides an on-orbit laboratory that enables human life science researchers to study and evaluate the physiological, behavioral, and chemical changes induced by spaceflight. Research performed using HRF-2 provides data to help scientists understand how the human body adapts to long-duration spaceflight.
MSL SCA-Batch3a-ESA CETSOL: A crewmember removed the used MSL Sample Cartridge, installed the next Furnace Calibration Cartridge, and prepared the facility for the next experiment run. The Materials Science Lab Batch 3a (MSL SCA-Batch 3a-ESA) serves two projects investigating how different phases organize in a structure when metallic alloys are solidified. The Microstructure Formation in Casting of Technical Alloys under Diffusive and Magnetically Controlled Convective Conditions (MICAST) experiment aims to deepen the understanding of the physical principles that govern solidification processes in metal alloys. The Columnar-to-Equiaxed Transition in Solidification Processing (CETSOL) experiment aims to deepen the understanding of the physical principles that govern solidification processes in metal alloys.
Rodent Research-Demonstration 1 (RR-D1): The crew restocked the Rodent Habitats with new foodbars. The crew then cleaned the lid and interior cage of the Rodent Habitat, access unit, and cameras. RR-D1 validates equipment and procedures for surgical techniques related to the wound healing process. Normal skin function and wound healing are important for maintaining good health, but spaceflight may impair healing of wounds in astronauts. Results from this investigation are intended to support design of a subsequent study on the effects of spaceflight on wound healing.
Small Optical Communication System (SOLISS): A crewmember removed the SOLISS hardware from the EFU Adapter on JEMAL Slide Table. The crew then installed the Low Power Wide Area Receiver onto the EFU Adapter. The SOLISS hardware demonstrates the use of an optical system with power, communication, and cooling provided by an EFU Adapter, which is a Japanese Experiment Module (JEM) exposed facility platform interface. SOLISS technology allows transmission of large amounts of data from the space station, as well as from satellites in Geostationary Orbit (GEO), to ground stations.
The ISS Experience: The crew performed the final stow of The ISS Experience EVA Z-Cam. The ISS Experience is a cinematic virtual reality (VR) series documenting life and research aboard the space station. Filmed over multiple months, the immersive VR series documents different crew activities – from science conducted aboard the station to preparation for a spacewalk.
Systems:
Environmental Health System (EHS) Acoustic Monitoring: Crew-held acoustic monitors were used to take acoustic measurements at specified locations on ISS. The acoustic monitoring sessions gather data to characterize any changes to the acoustic environment throughout the station.
EHS Total Organic Carbon Analyzer (TOCA) Water Recovery System (WRS) Sample Analysis & Data Record: The crew performed an analysis of the water processing assembly (WPA) using the TOCA. The TOCA unit oxidizes organic carbon species present in the water to carbon dioxide gas and measures the concentration using nondispersive infrared spectroscopy. Analysis of the potable water using the TOCA occurs on a weekly basis.
Cargo Dragon Cargo Operations: The crew performed cargo transfer operations for Cargo Dragon SpaceX-23 (SpX-23). SpX-23 undock is scheduled for September 30th to return cargo and payloads to the ground.
Completed Task List Activities:
WHC KTO replace
Photo/TV AVN443 HD Encoder Ethernet Cable Swap
Today’s Ground Activities:
All activities are complete unless otherwise noted.
Crew Dragon Quiescent weekly checkout
Payload Rack Officer (PRO) Combustion Integration Rack (CIR) activation
JEM Airlock (JEMAL) activation
Look Ahead Plan
Thursday, September 23 (GMT 266)
Payloads:
BIOMOLE ops part 3 (NASA)
EarthKAM 85mm Lens Change (NASA)
Eklosion Message and Photo (ESA)
ESA EPO- Touch Surface (ESA)
Lumina Data Transfer (ESA)
Microbial Tracking 3 Sample Collect (NASA)
RR-D1 3A Biopsy (NASA)
STaARS BS12 Sample Removal and MELI insert (NASA)
Standard Measures Presleep Questionnaire (NASA)
Systems:
64S relocate training
Dragon cargo ops
EVA Battery charge terminate
Friday, September 24 (GMT 267)
Payloads:
BIOMOLE MinION hardware stow (NASA)
EarthKAM Node 2 Shutdown and stow (NASA)
Food Acceptability (NASA)
HRF1 PC1 Troubleshoot (NASA)
ISS HAM pass (NASA)
Microbial Tracking 3 Sample collect with video (NASA)
Mochii Hardware removal (NASA)
PILOTE VR Troubleshoot (ESA)
RR-D1 3B Biopsy (NASA)
Standard Measures Postsleep Questionnaire (NASA)
Thermal Amine Sampling (NASA)
Systems:
ISS deboost
Dragon cargo ops
Saturday, September 25 (GMT 268)
Payloads:
NanoRacks Module-9 Ops 4 (NASA)
Standard Measures Saliva setup (NASA)
Systems:
Crew off-duty
Today’s Planned Activities:
All activities are complete unless otherwise noted.
Environmental Health System (EHS) Acoustic Monitor Setup
Dreams data transfer
JEM Airlock Slide Table (ST) Extension to JPM Side
Combustion Integrated Rack Manifold #4 Bottle Replacement
SOLISS Removal from EFU Adapter
Acoustic Monitor Setup for Static Measurements
ISS Experience EVA Z-Cam Final Stow
EMER Air cryo glove relocate
Low Power Wide Area Receiver Installation to EFU Adapter
EDV Build
In-Flight Maintenance (IFM) Floating Potential Measurement Unit (FPMU) Disassembly
Environmental Health System (EHS) Total Organic Carbon Analyzer (TOCA) Water Recovery System (WRS) Sample Analysis
JEM Airlock Slide Table (ST) Retraction from JPM Side
Environmental Health System (EHS) – Microbial Capture Device (MCD) and Coliform Water Sample Analysis 44 +/- 4 hours post processing
Material Science Laboratory Calibration Cartridge Insertion
Polar Desiccant Swap
Cargo Transfer to Dragon
Microbial Tracking-3 Environmental Sample Collection
Microbial Tracking-3 Sample Iceberg Insert
Public Affairs Office (PAO) Event in High Definition (HD) in Columbus
HRF Rack 2 Rack Handle Removal and Replacement
Environmental Health System (EHS) Total Organic Carbon Analyzer (TOCA) Sample Data Record
Crew Dragon Tablet Sync
Environmental Health System (EHS) – Surface Sampler Kit (SSK) and Microbial Air Sampler (MAS) Analysis T + 5
Crew Handover Conference
Environmental Health System (EHS) Total Organic Carbon Analyzer (TOCA) Waste Water Bag (WWB) Changeout








