ispace Completes Lunar Orbit Insertion Maneuver

The Mission 1 Lander performed its first lunar orbit insertion maneuver in accordance with the mission operation plan, at 10:24 (JST), on March 21, 2023, under the direction of ispace engineers at the HAKUTO-R Mission Control Center in Nihonbashi, Tokyo. After a controlled burn from the lander’s main propulsion system lasting several minutes, the maneuver was successfully completed.
In general, all orbital control operations for Mission 1 have been completed as planned following launch. While the lander has performed multiple deep space maneuver operations, this maneuver represents the longest burn performed by the propulsion system during the mission. These functions during the approximately three-month period verify that the lander performs as designed and demonstrates the high operational capability of ispace engineers to perform long-term mission operations.
The achievement demonstrates ispace’s ability to successfully deliver spacecraft and payloads into a stable lunar orbit. The successful insertion of the lander into lunar orbit is an important step toward the establishment of a payload transportation service, as it demonstrates that ispace is capable of transporting customer payloads to orbit around the Moon. Future ispace missions will involve deployment of satellites into lunar orbit.
Currently, ispace is in active negotiations with a number of global companies regarding future lunar missions, many of which have identified demand not only for lunar landings but also for transportation to orbit around the Moon.
During Mission 3, two relay satellites are planned to be injected into lunar orbit to establish communications with the landing site on the far side of the Moon. The valuable data and know-how gained from today’s operation is being incorporated into mission planning for Mission 3 in order to enhance technical reliability.
The completion of all lunar orbital maneuvers prior to the beginning of the landing sequence—Success 8 of the Mission 1 Success Milestones—is scheduled to be announced around late-April 2023. The lunar landing, Success 9, is then scheduled to take place around late-April 2023. Specific information on date and time of the landing will be announced in the future.
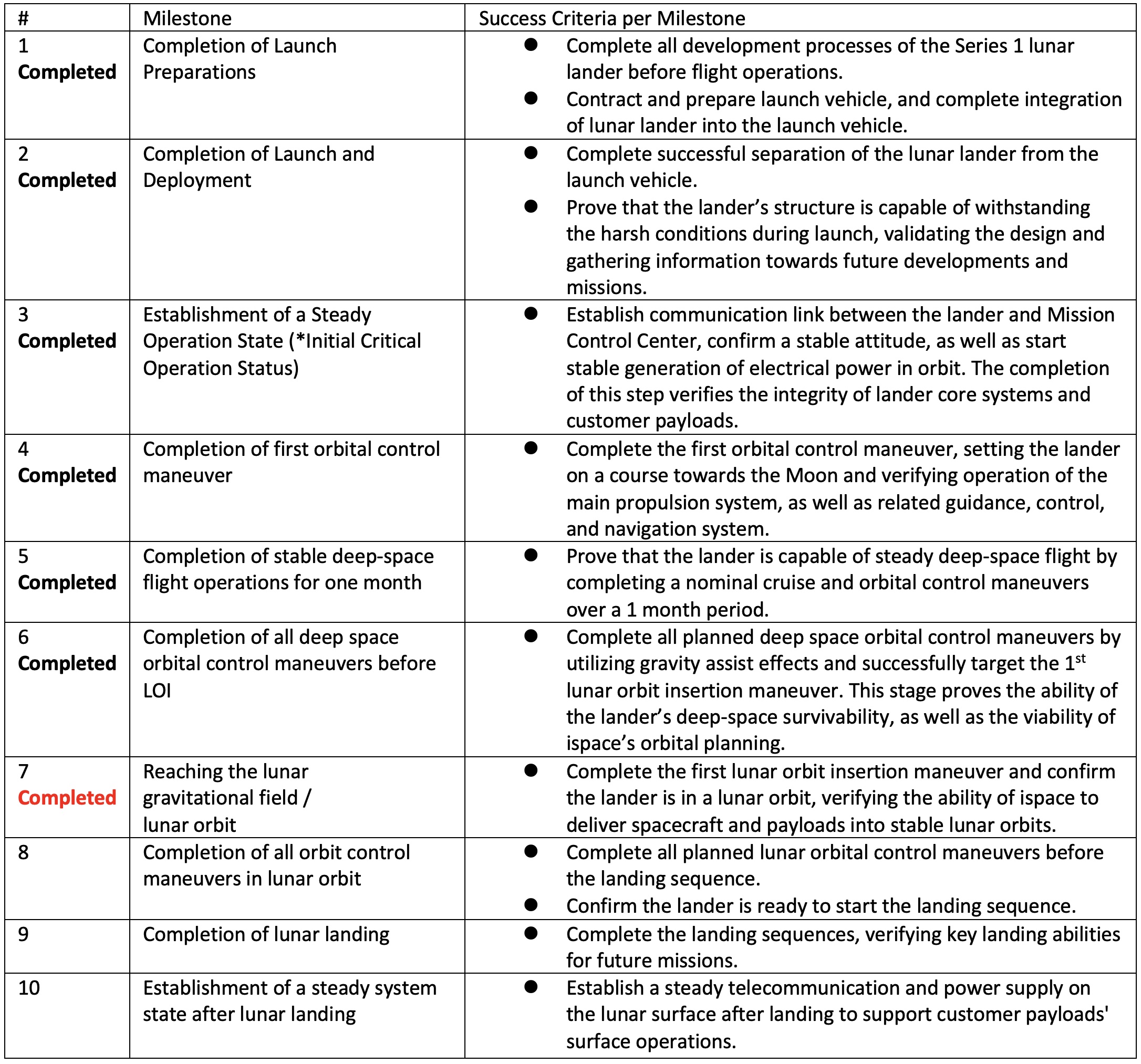
Mission 1 Milestones
For Mission 1, ispace has set 10 milestones between launch and landing, and aims to achieve the success criteria established for each of these milestones. Recognizing the possibility of an anomaly during the mission, the results will be weighed and evaluated against the criteria and incorporated into future missions already in development between now and 2025. Mission 2 and Mission 3, which also will contribute to NASA’s Artemis Program, will further improve the maturity of ispace’s technology and business model. Future announcements on progress of milestone achievement are expected to be released once attained.
About ispace, inc.
ispace, a global lunar resource development company with the vision, “Expand our Planet. Expand our Future.”, specializes in designing and building lunar landers and rovers. ispace aims to extend the sphere of human life into space and create a sustainable world by providing high-frequency, low-cost transportation services to the Moon. The company has offices in Japan, Luxembourg, and the United States with more than 200 employees worldwide. ispace U.S. is part of a team led by Draper, which was awarded a NASA Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) Program contract to land on the far side of the Moon by 2025. Both ispace, and ispace EU were awarded contracts to collect and transfer ownership of lunar regolith to NASA, and ispace EU was selected by ESA to be part of the Science Team for PROSPECT, a program which seeks to extract water on the Moon.
Established in 2010, ispace operated “HAKUTO”, which was one of five finalist teams in the Google Lunar XPRIZE race. The company’s first mission as part of its HAKUTO-R lunar exploration program launched on Dec. 11, 2022, from the United States on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and is currently expected to land on the lunar surface at around late April 2023. Subsequent missions are in development with launches expected in 2024 and 2025. ispace has also launched a lunar data business concept to support new customers as a gateway to conduct business on the Moon.
For more information, visit: www.ispace-inc.com; Follow us on Twitter: @ispace_inc.








