California Landslide Analyzed From Orbit
California Landslide
ESA,
On 20 May, over a million tonnes of dirt and rock buried part of California’s Highway 1 along the Pacific coastline in the state’s Big Sur region.
In addition to cutting off the route, the landslide added some 5 hectares of land to the shoreline.
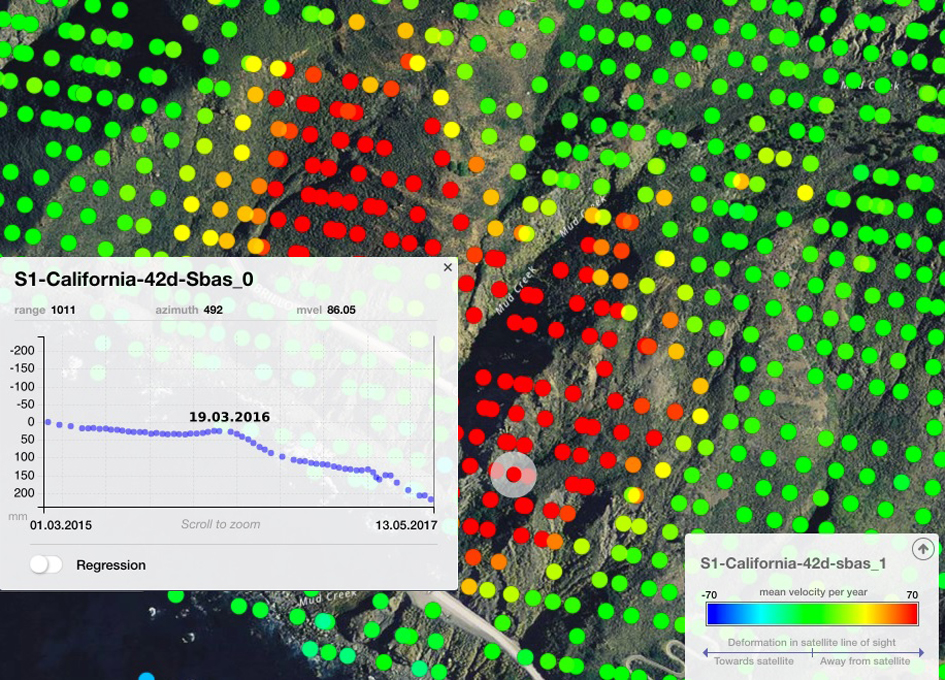
Sentinel-1’s radar shows that the ground that slid down the mountain was moving in the two years before the landslide.
The radar data were processed using Small Baseline Subset interferometry (SBAS), a technique that can detect and monitor movements over wide areas with high sensitivity. In this image, red dots represent points where the ground was moving away from the satellite at a rate of more than 70 mm per year. Green dots show stable ground in the surrounding area.








