Mars Odyssey THEMIS Image: Tantalus Fossae
 |
|
| The Science | The Story | |||
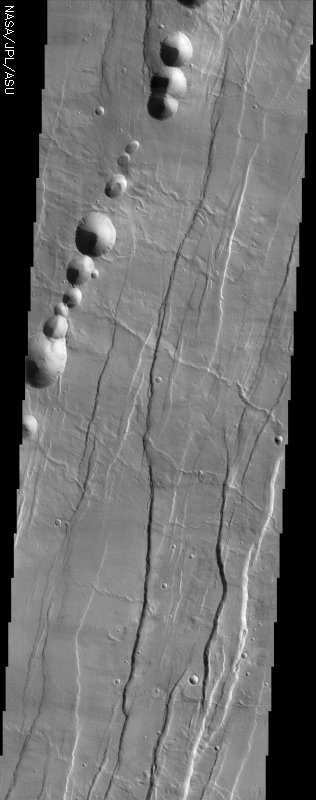
| Tantalus Fossae is a set of long valleys on the eastern side of Alba Patera. These valleys are referred to as grabens and are formed by extension of the crust and faulting. When large amounts of pressure or tension are applied to rocks on timescales that are fast enough that the rock cannot respond by deforming, the rock breaks along faults. In the case of a graben, two parallel faults are formed by extension of the crust and the rock in between the faults drops downward into the space created by the extension. Numerous sets of grabens are visible in this THEMIS image, trending from north-northeast to south-southwest. Because the faults defining the graben are formed parallel to the direction of the applied stress, we know that extensional forces were pulling the crust apart in the west-northwest/east-southeast direction. The large number of grabens around Alba Patera is generally believed to be the result of extensional forces associated with the uplift of Alba Patera. Also visible in this image are a series of linearly aligned pits, called a pit chain. The pits are not the result of impact cratering, but are similar to sinkholes on Earth. Sinkholes are typically formed by the removal of rock (commonly limestone) underground by groundwater — when enough rock is removed, the overlying rock becomes too heavy to be supported, and it collapses, forming a pit. Unlike sinkholes, however, the pit chains near Alba Patera were likely formed when empty underground lava tubes collapsed, accounting for the presence and alignment of many pits. Numerous channel features are also observed in the image, and follow the local topographic slope, which is downhill to the east-southeast. One of these, a long channel in the center of the image, nicely demonstrates the complex relations possible between geologic features. The geologist’s rule of superposition says that a feature on top of (superposing) another feature, or cutting across another feature is younger than the feature it covers or cuts. In one location, the channel cuts across the somewhat subdued fault defining a graben (near the right side of the image), indicating that the channel was carved after the graben was formed. But in other places (near the center of the image), the channel is clearly cut by a large fault defining one of the grabens, indicating that some faulting was occurring after the channel was carved. These relationships can be observed throughout this image. By mapping out superposition relationships in detail, geologists can establish a complex sequence of events that occurred long ago. [Source: ASU THEMIS Science Team] | The first thing that catches your eye in the image above is a string of round pits that are strewn dramatically on the surface. Although they may look like craters, nothing came hurtling in from the sky to make them. Instead, collapses along a lava tube have created this long dotted line on the Martian surface. The lava tube, a hollow feature beneath the surface, can’t always withstand the weight from above, and so collapses in places, forming pits like the ones seen here.
Throughout the rest of the image are a series of depressed valleys known as grabens that run roughly from the northeast to the southwest. They formed when the crust of the Martian surface was stretched so fast that it broke along faults. When that happened, the rock in between fell downward into the space created by the extension, creating the long subtle streaks of lowered terrain. They were probably created when Alba Patera, the shield volcano of this area, was elevated or “uplifted” through tectonic forces. This area of long valleys is named after Tantalus, a king of ancient Lydia who, according to legend, betrayed the gods and was sent to Hades. In this subterranean place, he was forced to stand in water up to his chin underneath the branches of fruit trees. Every time he tried to drink, the water would recede, and every time he tried to eat, the boughs would move the fruit just out of reach. You can easily see where the word “tantalize” comes from. Scientists are intrigued so much by the history of this area that they seek to understand its elusive past. Luckily, their interests are much more in reach than those of poor Tantalus. A number of channels in this image (running downhill from the west-northwest to the east-southeast) help them understand the chain of events that worked to create the compelling features in this region. Take a look at the channels close-up and see if you can tell whether the channels or the grabens happened first. A rule of thumb is that if one feature is on top of another or cuts across it, it is younger than the feature it covers or cuts. One of the channels in the center of the image is great to study. Toward the right side of the image, the channel cuts across a fault, indicating it formed before the graben. Follow the channel westward, however, and you’ll see that a large fault cuts the channel, indicating that this graben formed after the channel. That probably means this criss-crossed region went through a seeming eternity of torture itself, as the land kept tearing and stretching, as channels were carved and recarved, as lava tubes formed and then finally collapsed, only to have their walls erode in further streaks as well. [Questions? Email marsoutreach@jpl.nasa.gov] [Source: NASA/JPL Mars Outreach] | |||
NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory manages the 2001 Mars Odyssey mission for NASA’s Office of Space Science, Washington, D.C. The Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS) was developed by Arizona State University, Tempe, in collaboration with Raytheon Santa Barbara Remote Sensing. The THEMIS investigation is led by Dr. Philip Christensen at Arizona State University. Lockheed Martin Astronautics, Denver, is the prime contractor for the Odyssey project, and developed and built the orbiter. Mission operations are conducted jointly from Lockheed Martin and from JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena.
Image Credit: NASA/JPL/Arizona State University
| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Latitude | 38.2 |   | Instrument | VIS |
| Longitude | 103.8W (256.2E) |   | Resolution (m) | 19 |
| Image Size (pixels) | 3007×1189 |   | Image Size (km) | 57.1×22.6 |









